Piles: Symptoms, Causes and Treatments:
Piles are hemorrhoids that become inflamed. Hemorrhoids are masses, clumps, cushions of tissue in the anal canal - they are full of blood vessels, support tissue, muscle and elastic fibers.
Although hemorrhoids are thought of as unpleasant inflammations, we all have them.1 It is when the hemorrhoidal cushions become too big (inflamed) that problems occur - when this happens they are called piles or pathological hemorrhoids.2
Contents of this article:
You will also see introductions at the end of some sections to any recent developments that have been covered by MNT's news stories. Also look out for links to information about related conditions.
Fast facts on piles
Here are some key points about piles. More detail and supporting information is in the main article.
- Piles are hemorrhoids that become inflamed.
- The size of piles can vary and are found inside or outside the anus.
- Half the US population are affected by piles, usually before the age of 50.4
- Around 10% of patients who go and see their doctor about piles, require surgical treatment.2
- Piles are often not serious and go away on their own.5
- Internal hemorrhoids are ordered into four grades.7
- External hemorrhoids are called perianal hematoma.
- Piles occur due to chronic constipation, chronic diarrhea, lifting heavy weights, pregnancy or straining when passing a stool.
- A doctor can usually diagnose piles rapidly on examination.
- For grades 3 or 4 hemorrhoids, surgery may be necessary.
What are piles?
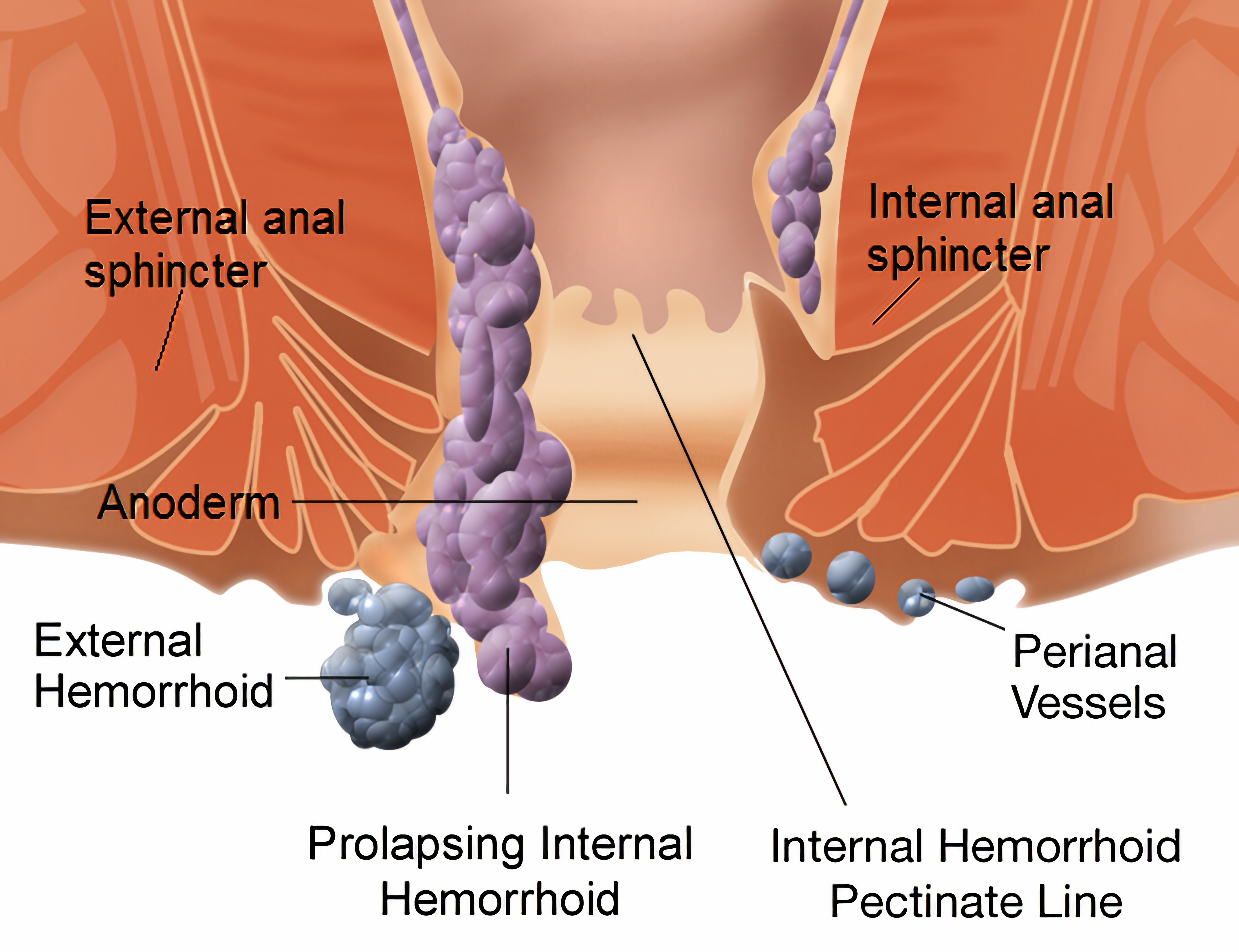
Piles can be of various sizes and may be internal (inside the anus) or external ones (outside the anus). Typically, internal piles occur from 2 to 4cm above the opening of the anus. External piles (perianal hematoma) occur on the outside edge of the anus. The internal ones are much more common.3
According to the US National Institutes of Health (NIH), symptomatic hemorrhoids affect at least half the American population at some time in their lives before the age of 50.4
In the majority of cases, piles are effectively treated with over-the-counter medications, a good fluid intake, and by following a diet high in fiber. In severe cases, the piles may have to be surgically removed. About 10% of patients who go and see their doctor about piles eventually require surgical intervention.2
Symptoms of piles
In most cases piles are not serious and go away on their own after a few days.5
An individual with piles may experience the following symptoms:6
- A hard lump may be felt around the anus. It consists of coagulated blood, called a thrombosed external hemorrhoid. This can be painful
- After going to the toilet, a feeling that the bowels are still full
- Bright red blood after a bowel movement
- Itchiness around the anus
- Mucus discharge when emptying the bowels
- Pain while defecating
- The area around the anus may be red and sore.
Internal hemorrhoids are classified into four grades:7
- Grade 1 - there are small inflammations, usually inside the lining of the anus. They are not visible
- Grade 2 - larger than grade 1 hemorrhoids, but also inside the anus. When passing a stool, they may get pushed out, but return unaided
- Grade 3 - often called 'prolapsed hemorrhoids'; these appear outside the anus. The patient may feel them hanging out. They can be pushed back in if the patient presses with their finger
- Grade 4 - these cannot be pushed back in and need to be treated by a doctor. They are large and stay outside the anus all the time.
External hemorrhoids are called perianal hematoma. These are small lumps that are located on the outside edge of the anus. They are very itchy and can be painful if a blood clot forms inside (thrombosed external hemorrhoid). Thrombosed external hemorrhoid requires medical treatment straight away.8
No comments:
Post a Comment